Coma Recovery Scale-Revised (CRS-R)
(Giacino et al., 2020)
Standardized neurobehavioral assessment designed for use in patients with disorders of consciousness. Used to establish a diagnosis, monitor behavioral recovery, predict outcomes, and assess treatment effectiveness. Can be helpful and guide goal writing (i.e., write goals based on what the patient is able to do or use metrics such as # of trials to increase the challenge).
Target Population
Patients with traumatic and non-traumatic DoC, are not communicating reliably and are functioning between RLAS Levels I-IV. The CRS-R is normed for patients aged 17-79. The pediatric version can be used when assessing children between the ages of 1-5 who have not yet completed language and motor development.
Descriptions
6 subscales comprised of hierarchically-arranged items reflecting brainstem (lowest item on subscale), subcortical, and cortically-mediated behaviors (highest item on subscale):
Auditory: movement to command; localization to sound; auditory startle; none
Visual: object recognition; object localization; visual pursuit; fixation; visual startle; none
Motor: functional object use; automatic motor response; object manipulation; localization to noxious stimulation; flexion withdrawal; abnormal posturing; none/flaccid
Oromotor: intelligible verbalization; vocalization/oral movement; oral reflexive movement; none
Communication: functional; non-functional; none
Arousal Functions: attention; eye-opening without stimulation; eye-opening with stimulation; unarousable
Testing Items
2 common objects (i.e., cup, comb, toothbrush)
Any object that makes a loud noise
ADL objects (i.e., toothbrush, phone)
Hand mirror
Bright colored object
Baseball sized ball
Pencil
Tongue depressor
Scoring
Standardized based on the presence or absence of operationally-defined behavioral criteria. The behavioral response must be clearly discernible before they are scored present. A score of 10 or greater indicates a diagnosis of Minimally Conscious State (MCS) or emergence from Minimally Conscious State (eMCS). Minimum score: 0 / Maximum score: 23
When should you discontinue the CRS-R?
When all 3 of the following behaviors have been elicited, concurrently, on 3 consecutive examinations conducted over 2 weeks:
Consistent movement to command (Auditory Subscale = 4)
Reliable yes-no responses (Communication Subscale = 2)
Focused attention (Arousal Subscale = 3)
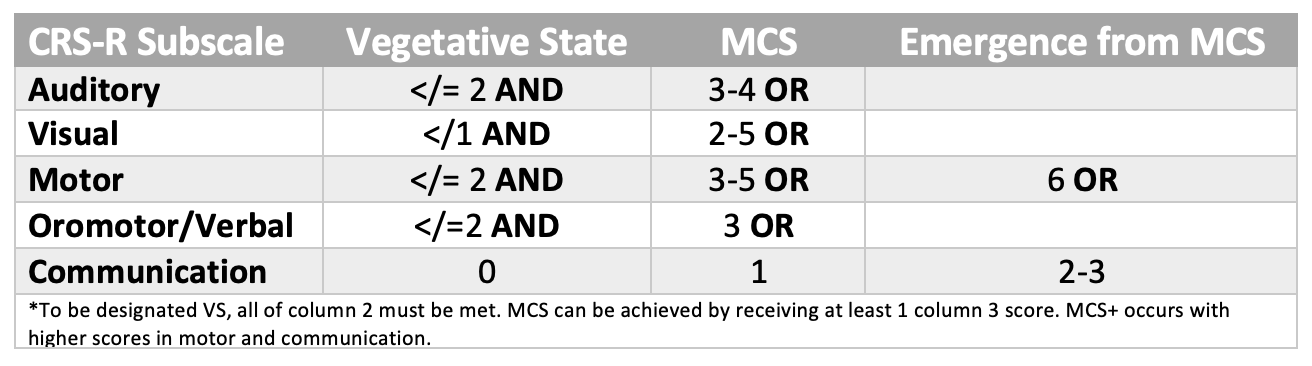
Criteria for Vegetative State (VS) and Minimally Conscious State (MCS)
Note. Adapted from “The JFK coma recovery scale-revised: Measurement characteristics and diagnostic utility”, by J. T. Giacino et al., 2004, Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, 85(12), p. 2023 (doi: 10.1016/j.apmr.2004.02.033). Copyright 2004.
Guidelines
Goal: prolong the length of time the patient maintains arousal
Administered anytime the patient is observed to: exhibit sustained eyelid closure AND/OR stops following commands for a period of at least one minute
Re-administer the arousal facilitation protocol when: sustained eye closure re-occurs OR behavioral responsiveness ceases despite sustained eye opening
References
Giacino, J. T., Bodien, Y. G., & Chatelle, C. (2020). CRS-R Coma Recovery Scale-Revised: Administration and scoring guidelines. https://www.tbims.org/combi/crs/CRS%20Syllabus.pdf
Giacino, J. T., Kalmar, K., & Whyte, J. (2004). The JFK Coma Recovery Scale-Revised: Measurement characteristics and diagnostic utility. Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, 85(12), 2020–2029. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apmr.2004.02.033